Nephrology
Nephro Logy

Nephrology for iMed Billing
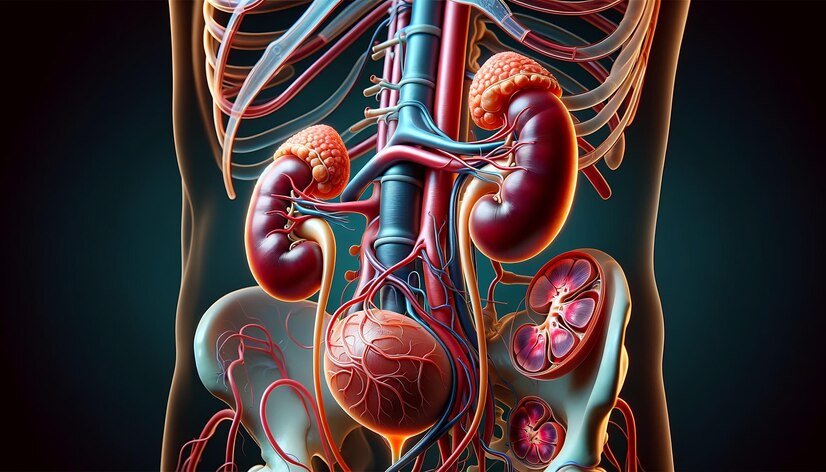
Nephrology is a medical specialty focused on kidney and the diagnosis, color of urine, treatment, and management of kidney diseases and related disorders. Nephrologists, the doctors who practice nephrology, address conditions such as chronic-kidney disease, acute-kidney injury, glomerulonephritis, hypertension related to kidney issues, and electrolyte imbalances. They are also involved in the management of patients requiring dialysis and kidney transplantation. Nephrologists perform a variety of diagnostic tests, including blood and urine tests, kidney biopsies, and imaging studies. Treatment strategies often involve medications, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, dialysis or transplantation. Nephrology also overlaps with other medical disciplines, given the kidney's role in regulating blood pressure, red blood cell production, and overall homeostasis. This field is crucial in improving and upgrading the quality of lifespan and survival rates for patients with kidney-related illnesses.
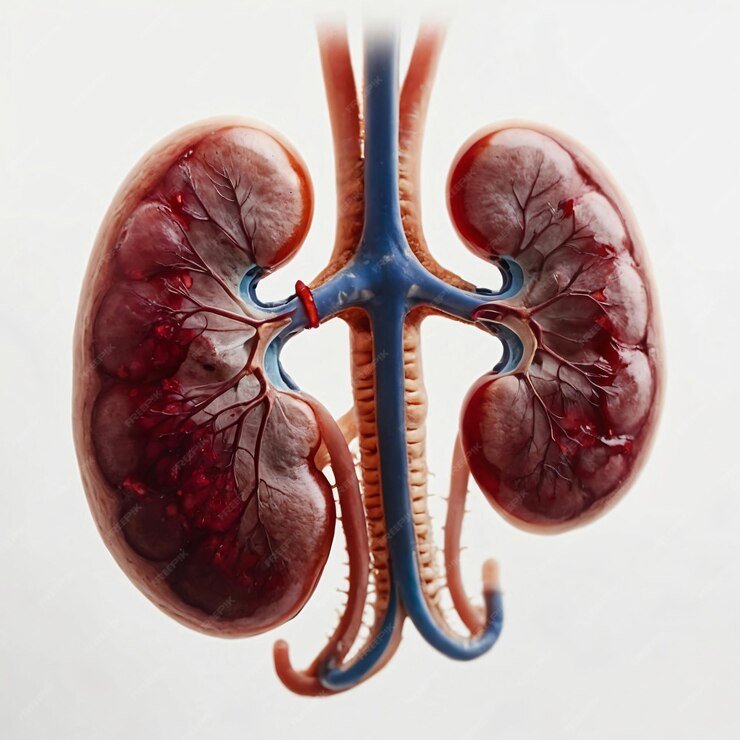
Kidney Functions

The kidneys are vital organs with several critical functions that maintain the body's overall health and homeostasis. Each kidney performs the following key roles

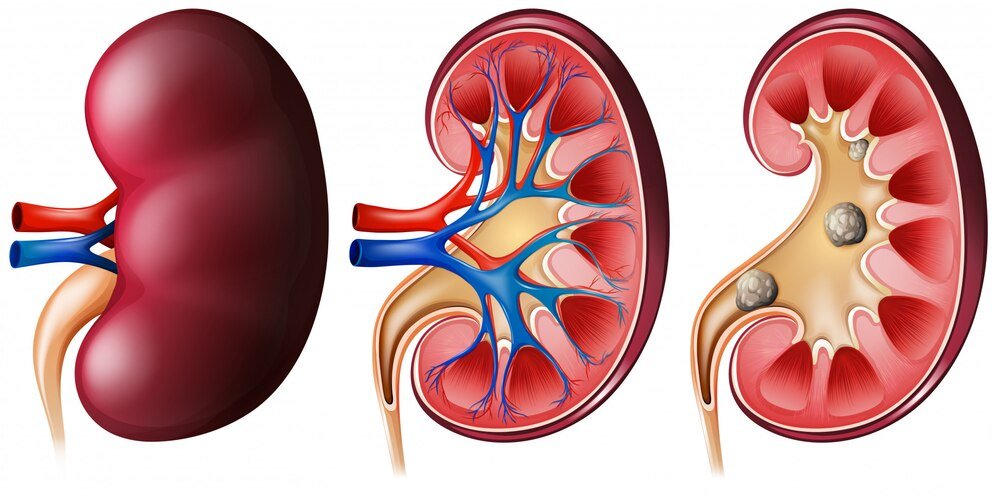
Detailed Components
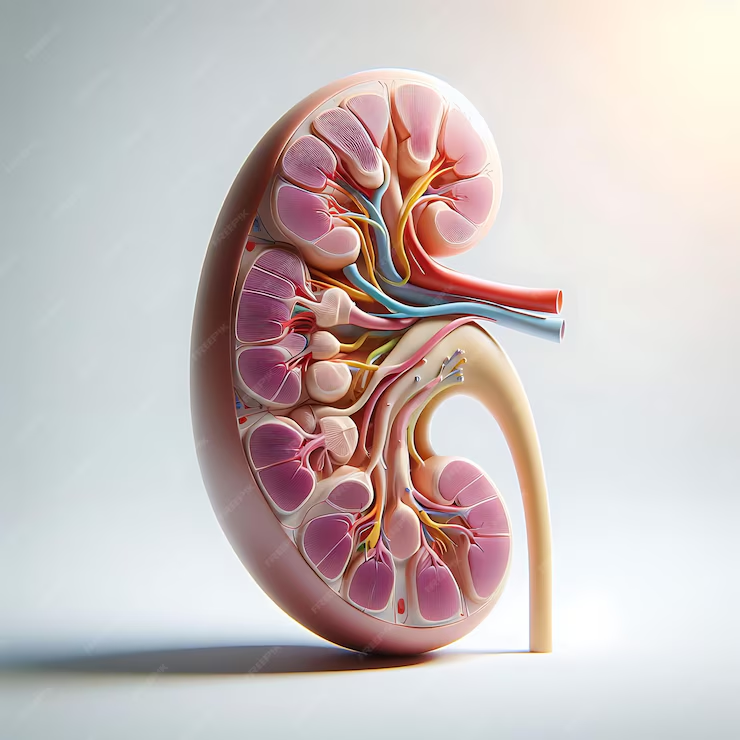
Filtration of Blood
The kidneys play a pivotal role in blood purification, filtering out waste products and surplus substances to maintain bodily balance. Within the kidneys, nephrons act as the essential units, sieving blood as it passes through
Regulation of Blood Pressure
The kidneys help regulate blood pressure through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS). They release the enzyme renin, which activates a cascade of hormones that adjust blood vessel constriction and sodium and water balance, thus controlling blood pressure.
Electrolyte Balance
The kidneys maintain the balance of critical electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphate in the blood. They achieve this by filtering these electrolytes and either reabsorbing the necessary amounts back into the bloodstream or excreting excess quantities in the urine.
Acid-Base Balance
The kidneys help regulate the body's pH level by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate from urine. This function is crucial in maintaining the acid-base balance, preventing conditions like acidosis or alkalosis.
Excretion of Metabolic Waste
The kidneys remove metabolic waste products from the bloodstream, including urea (from protein metabolism), uric acid (from nucleic acid metabolism), and creatinine (from muscle metabolism). These waste products are excreted/pass in the urine.
Water Balance
The kidneys regulate the body's fluid balance/footing by adjusting the amount of water excreted in the urine. This function helps maintain optimal hydration levels and blood volume.
Red Blood Cell Production
Erythropoietin is a hormone secreted by the kidneys that causes the bone marrow to produce red blood cells. Particularly when blood oxygen levels are low, this mechanism is essential for avoiding anemia

Detoxification
The kidneys help detoxify the body by excreting drugs, toxins, and other harmful substances. They play a critical role in metabolizing and eliminating these compounds from the bloodstream.
Vitamin D Activation
The kidneys convert inactive vitamin D into its active form, calcitriol. Active vitamin D is essential and crucial for calcium absorption in the intestines and for maintaining healthy bones.
Gluconeogenesis
The kidneys contribute to glucose production during periods of prolonged fasting or starvation by performing gluconeogenesis, the process of synthesizing glucose from noncarbohydrate sources.
Kidney Diseases
-
Chronic Kidney Disease
A long-term condition where the kidneys gradually/slowly lose function over time. It's often caused by diabetes, high blood pressure, and other chronic conditions.
-
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a rapid decline in your kidneys' ability to function, happening within hours or days. This sudden drop disrupts waste removal from your blood, leading to a build-up of toxins and potentially harming other organs
-
Glomerulonephritis
inflammation of the kidney's microscopic filtering units, called glomeruli. Infections, autoimmune disorders, or other underlying medical issues may be the cause of this syndrome.
-
Polycystic Kidney Disease
an inherited condition marked by the development of many kidney cysts. The kidneys may get larger and less functional as a result of these cysts.
-
Kidney Stones
Hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. Kidney stones can cause severe pain and create lot of trouble may lead to infection or kidney damage if not treated.
Urinary Tract Infections
Infections that affect the urinary system, including the kidneys (pyelonephritis). If left untreated, UTIs can lead to kidney damage.
Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetes-related renal damage. Over time, high blood sugar levels might impair the kidneys' ability to filter substances
Hypertensive Nephropathy
renal damage brought on by long-term excessive blood pressure. The elevated pressure may harm the kidneys' blood arteries, impairing their capacity to operate as intended.
Nephrotic Syndrome
A group of symptoms indicating kidney damage, including proteinuria (high levels of protein in the urine), hypoalbuminemia (low blood albumin levels), and edema (swelling).
-
Interstitial Nephritis
Inflammation of the kidney's interstitial tissue, which surrounds the nephrons. This can be caused by infections, medications, or autoimmune diseases
-
Alport Syndrome
A genetic disorder characterized by kidney disease, hearing loss, and eye abnormalities. It affects the basement membranes in the kidneys, ears, and eyes
-
Lupus Nephritis
Kidney inflammation caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. The immune system may attacks the kidneys, leading to inflammation and damage.
-
Minimal Change Disease
A disorder causing nephrotic syndrome, primarily seen in children. Despite severe symptoms, the kidneys appear normal under a regular microscope



Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Scarring in parts of the kidneys' glomeruli, which can lead to nephrotic syndrome and progressive kidney damage
Amyloidosis
A condition in which amyloid proteins build up in organs, including the kidneys, impairing their function.
Goodpasture Syndrome
A rare autoimmune disease where antibodies attack the kidneys and lungs, leading to bleeding in the lungs and glomerulonephritis.
Medullary Sponge Kidney
A congenital disorder where cysts form in the tubules within the kidneys, often leading to kidney stones and infections
-
Renal Artery Stenosis
Narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys, often caused by atherosclerosis, leading to high blood pressure and reduced kidney function
-
Hydronephrosis
Swelling of a kidney due to a buildup of urine, which can be caused by a blockage in the urinary tract
-
Wilms Tumor
A rare kidney cancer primarily affecting children, also known as nephroblastoma.

Treatments of Kidney Diseases


Lifestyle Modifications
Diet: Low sodium, low protein diets to reduce kidney workload. Exercise: Regular physical activity to manage blood pressure and diabetes. Smoking Cessation: To improve overall health and slow disease progression
Medications
Blood Pressure Control: ACE inhibitors or ARBs to manage hypertension. Diabetes Management: Medications like insulin or metformin to control blood sugar levels. Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs: Statins to reduce cardiovascular risk
Dialysis
Hemodialysis: Blood is filtered outside the body using a machine. Peritoneal Dialysis: The lining of the abdomen (peritoneum) filters blood inside the body
Kidney Transplant
Surgical procedure to replace a diseased kidney with a healthy donor kidney
Acute Kidney Injury
-
Treating the Underlying Cause
Fluids and Electrolytes: Intravenous fluids to address dehydration or shock. Medications: To treat infections or manage underlying conditions like heart failure.
-
Dialysis
Temporary measures to remove toxins and support kidney function during recovery.
-
Monitoring and Supportive Care
Regular monitoring of kidney function and supportive measures to prevent complications.

Glomeru lonephritis
Medications
Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation. Immunosuppressants: To control the immune response. Antibiotics: If infection is the cause.
Lifestyle Changes
Low-sodium diet to control blood pressure. Fluid restrictions in severe cases
Dialysis
In severe or advanced cases where kidney function is critically impaired.
Polycystic Kidney Disease

Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers (avoiding NSAIDs, which can harm kidneys).
Blood Pressure Control:
ACE inhibitors or ARBs to manage hypertension.
Dialysis or Transplant:
In advanced stages, kidney function is severely reduced.
Kidney stones
Medications
Pain relievers to manage symptoms. Alpha-blockers to help pass stones
Hydration
Increased fluid intake to flush out stones.
Surgical Procedures
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): Using shock waves to break up stones. Ureteroscopy: Using a scope to remove stones. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: Removing large stones via a small incision in the back

Antibiotics
Antibiotics are prescribed based on the type of bacteria causing the infection
Hydration:
Increased the fluid intake to help flush out bacteria
Blood Sugar Control: Medications such as insulin or oral hypoglycemics.
Blood Pressure Control: ACE inhibitors or ARBs.
Lifestyle Changes: Healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation.
Hypertensive Nephropathy
Medications
ACE inhibitors or ARBs to control blood pressure. Diuretics to reduce fluid overload
Lifestyle Changes
Low-sodium diet, weight management, and regular exercise.
Medications
Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to reduce proteinuria. Diuretics to manage edema
Diet
Low-sodium, low-protein diet to reduce kidney strain.


Interstitial Nephritis
-
Treating the Underlying Cause
Discontinuing the offending drug or treating the infection.
-
Medications
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
-
Immunosuppressive Therapy
Corticosteroids and other immunosuppressants like cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate mofetil.
-
Blood Pressure Control
ACE inhibitors or ARBs
-
Plasmapheresis
To remove harmful antibodies from the blood
-
Immunosuppressive Therapy
Medications to suppress the immune system.

CPT Codes in Nephrology
Evaluation and Management (E/M) Codes
Office or other outpatient visit for the E&M of a patient with kidney-related issues, varying by complexity and level of service provided
Dialysis procedures, including hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, as well as related management and monitoring services.
Kidney transplant procedures, including donor nephrectomy and recipient nephrectomy.
Kidney biopsy procedures, including percutaneous and open approaches, with or without imaging guidance
Diagnostic ultrasound of the kidneys and renal vessels
Comprehensive metabolic panel and individual electrolyte tests, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate
Laboratory tests to assess renal function, including serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Hypertension Management Codes
Total hip arthroplasty.
This procedure, also known as hip replacement surgery, involves replacing a damaged main hip joint with a prosthetic implant.
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and related services.
Procedures for the placement, revision, or removal of vascular access devices for hemodialysis, including arteriovenous fistulas and grafts
Diagnostic and interventional procedures for renal artery angiography, including angioplasty and stent placement
Management and monitoring services for home dialysis patients, including peritoneal dialysis and home hemodialysis
Ultrasound guidance for renal or peritoneal dialysis access procedures
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedures for renal imaging and evaluation
At iMedbillingPro, we are aware of the challenges and suffering that healthcare providers encounter when delivering first-rate patient care.
Copyright © 2024 iMed Billing Pro All Rights Reserved.

