Surgical Practices
Surgical Practices

Surgical Practices for iMed Billing
Surgical practices are specialized procedures surgeons perform to treat various diseases and conditions. Medical professionals with considerable training in performing surgeries are known as surgeons. Surgeons come in a variety of forms, with every individual was an expert in a certain bodily part or type of procedure.
Surgeons
Surgeons are highly trained and skilled medical doctors specializing in performing operations to treat various diseases and injuries. After completing medical school, they undergo rigorous residency programs that provide in-depth training in specific surgical techniques and areas of the body, such as orthopedics, cardiothoracic, or neurosurgery. Their expertise includes preoperative diagnosis, surgical intervention, and postoperative care. Surgeons must stay updated with medical technology and procedure advancements to ensure patient outcomes. Their role often involves critical decision-making and precision, requiring technical skill and extensive medical knowledge. Collaboration with multidisciplinary teams is also crucial to comprehensive patient care.


Types of Surgical Procedures

Types of Surgical Procedures
Their role often involves critical decision-making and precision, requiring technical skill and extensive medical knowledge. Collaboration with multidisciplinary teams is also crucial to comprehensive patient care.


Detailed Components
Open Surgery
In order to reach the region that needs to be treated, a significant incision must be made in the body during standard surgery
Minimally Invasive Surgery
A more recent kind of surgery that is performed using tiny incisions and specialized instruments. Compared to open surgery, MIS techniques are frequently linked to shorter recovery times and less discomfort
Laparoscopic Surgery
A tiny incision is made to introduce a thin, illuminated tube into the body, and a laparoscope is employed. The procedure is carried out by the surgeon using tiny equipment and a visual display that shows the inside of the body
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery uses a robotic surgical system controlled by the surgeon. The surgeon provider sits at a console and uses joysticks and pedals to control the robotic arms that operate.
Endoscopic Surgery
A general term for any surgery that uses an endoscope, a thin, lighted tube inserted into the body through a small incision.
Surgical Teams Procedures
-
Anesthesiologist
A doctor who administers anesthesia to the patient before surgery and monitors the patient's vital signs during surgery.
-
Nurse Anesthetist
A registered nurse who has completed additional training to administer anesthesia.
-
Surgical Nurse
A registered nurse who provides care to the patient before, during, and after surgery.

Critical Components of Surgical Practices

Preoperative Care
Evaluation and Diagnosis: A thorough evaluation of the patient's medical or treatment history, physical examination, and diagnostic testing is performed to ascertain whether surgery is required.
Patient Preparation: Patient education, obtaining informed consent, and preoperative instructions such as fasting and medication adjustments
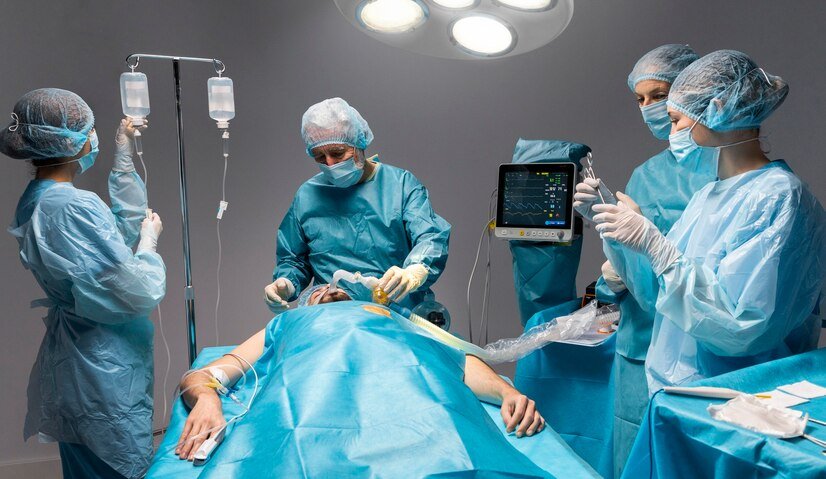



Detailed Components
Intraoperative Care
Surgical Team: Consists of the surgeon, anesthesiologist, surgical nurses, and sometimes surgical technologists and assistants, all working together to perform the procedure
Anesthesia
Administered to ensure the patient is unconscious and pain-free during the surgery. It can be general, regional, or local anesthesia.
Surgical Procedure
The actual operative intervention can range from minimally invasive techniques (like laparoscopy) to open surgeries.
Postoperative Care
-
Recovery
Monitoring the patient as they recover from anesthesia and the immediate postoperative period, ensuring stable vital signs
-
Pain Management
Administering medications and other therapies to manage postoperative pain.
-
Wound Care
Proper management of surgical sites to prevent infection and promote healing.
-
Follow-Up
Regular check-ups to monitor recovery progress and address any complications.


Common Surgical Specialties
General Surgery
Scope: Covers a broad range of procedures, primarily involving the abdomen (e.g., appendectomy, hernia repair, gallbladder removal). Skills: General surgeons are trained to handle various types of surgeries and emergencies
Cardiothoracic Surgery
Scope: Focuses on surgeries of the heart, lungs, esophagus, and other organs in the chest. Common Procedures include Coronary Artery Bypass Graft surgery (CABG), heart valve repair/replacement, and lung resection.
Orthopedic Surgery
Scope: Deals with the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Standard Procedures: Joint replacement (e.g., hip, knee), fracture repair, and spinal surgery





Detailed Components
Neurosurgery
Scope: Involves surgery of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Standard Procedures: Brain tumor removal, spinal fusion, and treatment of traumatic brain injury.
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Scope: Focuses on reconstructing face and bodily tissue deformities caused by disease, trauma, birth abnormalities, and burns. Common Procedures: Breast reconstruction, cleft lip/palate repair, and cosmetic surgery (e.g., rhinoplasty, facelift
Urological Surgery
Scope: Addresses surgical treatment of the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. Standard Procedures: Prostatectomy, kidney stone removal, and bladder surgery. Advancements in Surgical Practices
-
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Techniques: These include laparoscopic and robotic surgery, which uses small incisions and specialized instruments. Benefits: Reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and fewer complications
-
Robotic Surgery
System: Surgeons use robotic systems to perform precise and controlled movements. Applications: Common in urology, gynecology, and general surgery
-
Enhanced Recovery after Surgery
Protocol: A group of postoperative procedures designed to lessen surgical anxiety and speed up recuperation. Elements: Include optimal pain management, early mobilization, and nutritional support.


CPT Codes in Surgical Practices
General Surgery
Laparoscopic appendectomy.
This code covers the minimally invasive surgical removal of the appendix using a laparoscope, a small, lighted tube inserted through a tiny cutt in the abdomen
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
This code is used for the laparoscopic removal of the gallbladder, typically performed to treat gallstones and gallbladder inflammation.
Coronary artery bypass, using arterial graft(s).
This procedure involves bypassing one or more blocked coronary arteries using arteries from the patient's body, restoring blood flow to the heart
Aortic valve replacement.
This code describes the surgical replacement of the aortic valve, often necessary due to valve stenosis or regurgitation.
Orthopedic Surgery
Total hip arthroplasty.
This procedure, also known as hip replacement surgery, involves replacing a damaged main hip joint with a prosthetic implant.
Total knee arthroplasty.
This code is for the surgical replacement of the knee joint with a prosthesis, commonly performed to relieve severe arthritis or trauma damage.
Laminectomy for decompression of spinal cord.
This surgical procedure involves removing portion of the vertebra called the lamina to relieves pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Craniotomy for evacuation of hematoma.
This code covers the surgical removal of a hematoma (a blood collection) from within the brain, typically through an opening in the skull.
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
This procedure involves the placement of tissue expander under the skin and muscle after a mastectomy to prepare for a future breast implant
Rhinoplasty, primary, including major septal repair.
This code is for a primary nose reshaping surgery that also includes significant repair of the nasal septum, often to improve breathing as well as appearance.
Lithotripsy, extracorporeal shock wave.
This nonintrusive procedure uses shock waves to break up kidney stones into smaller ones that can pass through the urinary tract.
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
This surgical procedure involves removing portion of the prostate gland through the urethra to treat urinary problems due to an enlarged prostate.
At iMedbillingPro, we are aware of the challenges and suffering that healthcare providers encounter when delivering first-rate patient care.
Copyright © 2024 iMed Billing Pro All Rights Reserved.

